How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into the essential aspects of drone operation, from pre-flight checks and safety protocols to mastering flight controls and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll explore various flight modes, navigation techniques, and essential maintenance procedures, equipping you with the knowledge to confidently take to the skies.
We’ll cover everything from understanding your drone’s controls and navigating different environments to capturing professional-quality photos and videos. Learn about battery management, troubleshooting common issues, and adhering to important safety regulations to ensure a smooth and enjoyable flying experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. This involves inspecting various components and verifying compliance with local regulations. Failing to do so can lead to accidents, damage to property, or legal repercussions.
Drone Inspection, How to operate a drone
A comprehensive pre-flight inspection ensures the drone’s airworthiness. This involves visually inspecting key components and verifying their functionality.
| Component | Check | Component | Check |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Inspect for cracks, damage, or loose attachments. Ensure they spin freely. | Battery | Check battery level and ensure it’s securely connected. Inspect for any damage or swelling. |
| GPS Signal | Confirm a strong GPS signal is acquired before takeoff. Sufficient satellites should be locked. | Gimbal (if applicable) | Verify the gimbal moves smoothly and is securely mounted. Check for any unusual noises or vibrations. |
| Camera | Check the camera lens for smudges or obstructions. Confirm the camera is functioning correctly. | Flight Controller | Visually inspect for any damage or loose connections. Ensure all cables are securely plugged in. |
| Sensors | Check the condition of any sensors (e.g., ultrasonic, infrared) for any damage or obstructions. | Airframe | Inspect the drone’s body for any cracks, damage, or loose parts. |
Understanding and Adhering to Regulations
Operating a drone requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and airspace restrictions. Ignoring these rules can result in hefty fines or legal action. These regulations vary by country and even by region within a country.
Examples of prohibited areas include airports, military bases, and areas with restricted airspace. Flying near crowds or critical infrastructure (power lines, hospitals) is also typically prohibited.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to react in emergency situations is vital for safe drone operation. A loss of signal or malfunction can occur unexpectedly. Preparedness is key.
- Loss of Signal: Immediately initiate Return-to-Home (RTH) function if available. If RTH fails, attempt to manually control the drone back to a safe landing zone. Prepare for a potential emergency landing.
- Malfunction: Attempt to troubleshoot the issue based on the type of malfunction. If the issue persists, initiate RTH or attempt a controlled descent and landing. Prioritize safety over recovering the drone.
- Battery Failure: Initiate RTH immediately. If this fails, prioritize a safe landing as soon as possible. Low battery warnings should be heeded seriously.
- Unexpected Weather: Land the drone immediately if unexpected weather conditions (strong winds, rain, etc.) arise. Do not attempt to fly in adverse weather conditions.
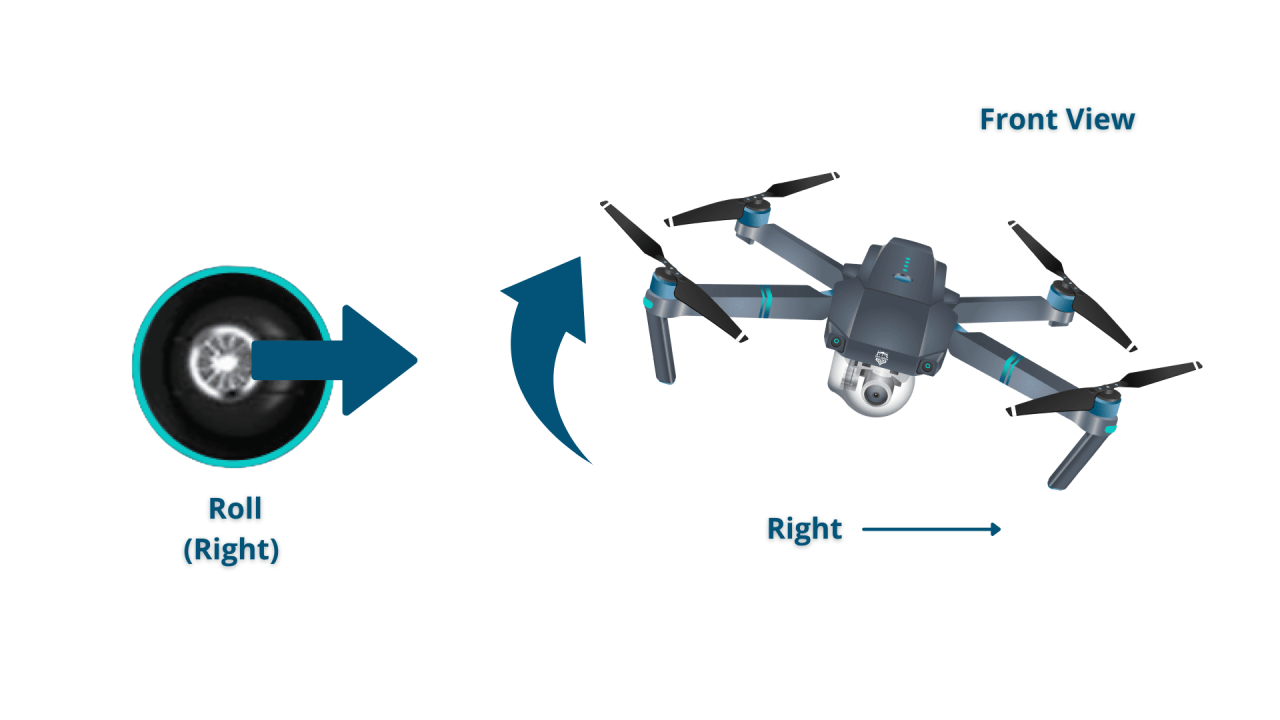
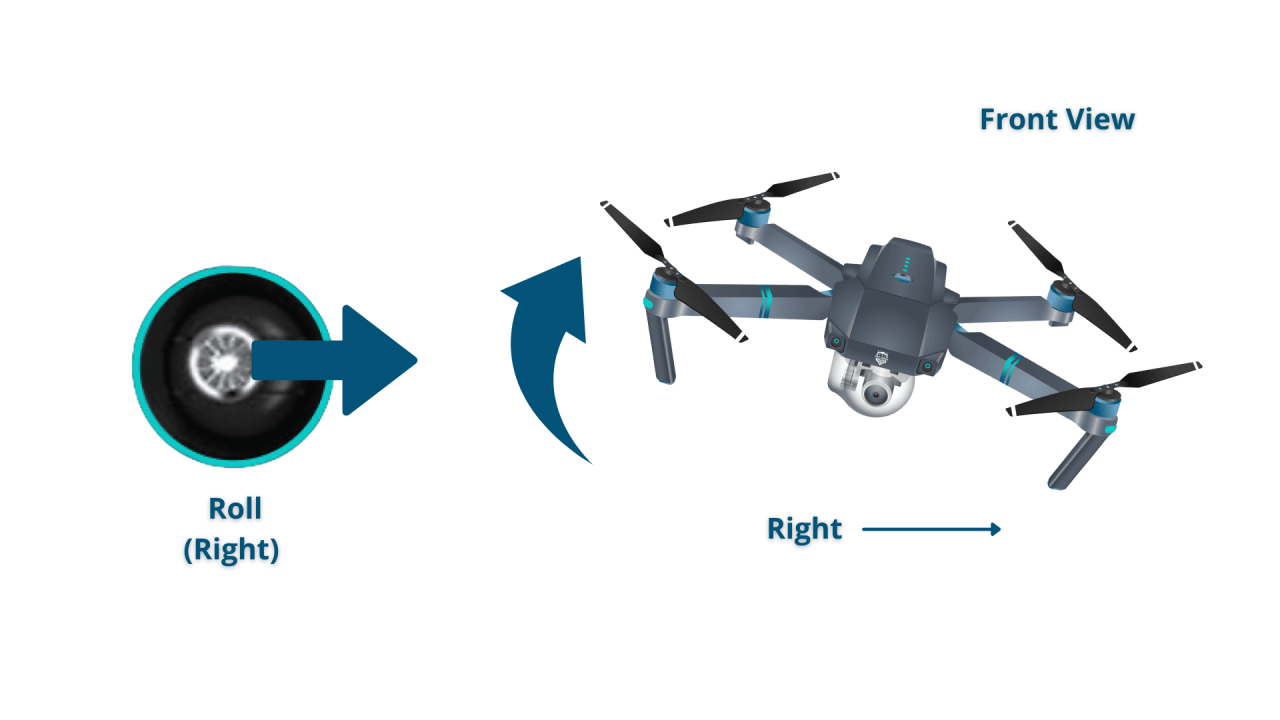
Understanding Drone Controls and Flight Modes
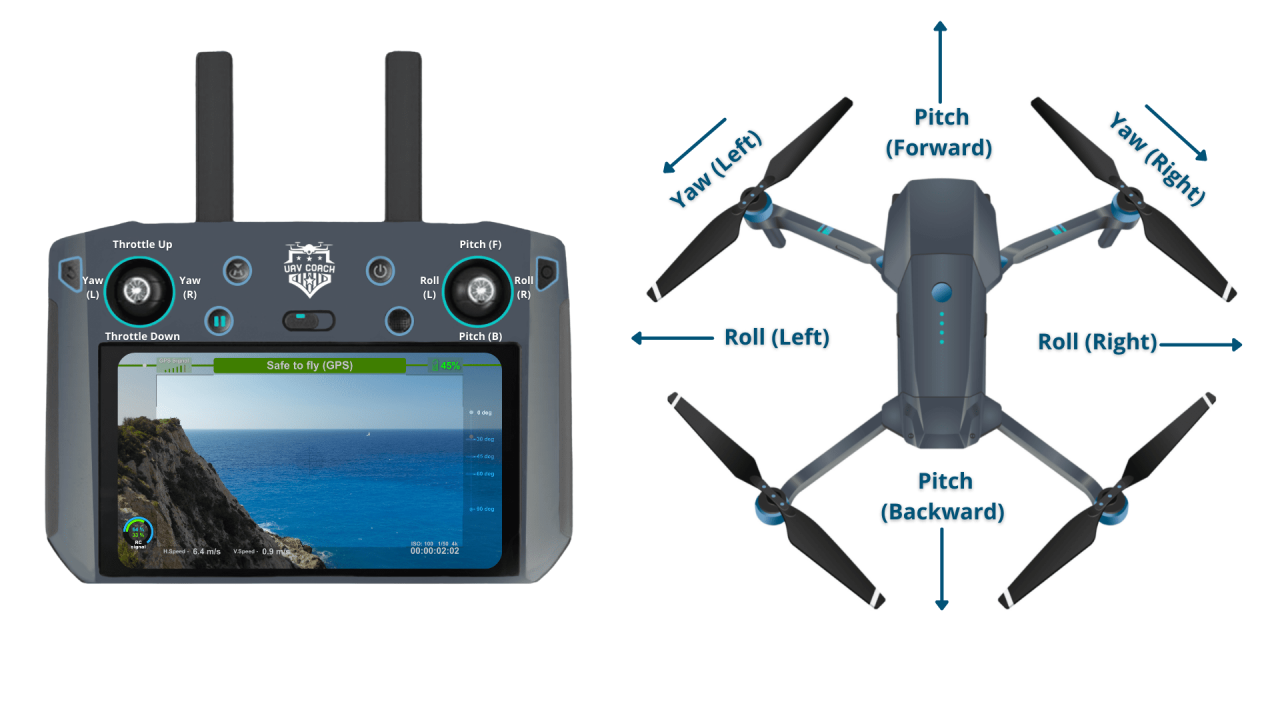

Effective drone operation hinges on understanding the drone controller and its various flight modes. Different controllers offer varying levels of control and features, while flight modes adapt to different flying situations.
Drone Controllers
Two common types of drone controllers are handheld transmitters and smartphone apps. Handheld transmitters provide more precise control and responsiveness, especially in challenging conditions. Smartphone apps, while convenient, might lack the precision and tactile feedback of dedicated controllers. Some drones offer both options.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and mastering basic maneuvers. Learning to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is a comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This will help you understand everything from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques, ensuring you operate your drone responsibly and efficiently.
Handheld transmitters generally offer more buttons and joysticks for precise control, allowing for fine adjustments of throttle, yaw, pitch, and roll. Smartphone apps rely on touchscreen controls, which can be less intuitive and responsive in complex flight maneuvers.
Flight Modes
Various flight modes cater to different flight scenarios and pilot skill levels. Understanding these modes is essential for safe and efficient drone operation. Improper use can lead to accidents.
GPS Mode: Maintains position using GPS, ideal for stable hovering and straightforward flight. It’s generally beginner-friendly.
Attitude Mode: Controls the drone’s attitude (pitch, roll, yaw) relative to its current orientation. Useful for precise maneuvers but requires more skill due to less stability.
Other modes include Sport Mode (for faster and more agile flight), Cine Mode (for smoother, cinematic shots), and Return-to-Home (RTH) for automated return to the launch point.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedure
A smooth takeoff and landing are essential for safe drone operation. Following a step-by-step procedure ensures a controlled and safe flight.
Pre-flight checks completePower on the drone and controller.Ensure GPS signal is acquired (if applicable).Slowly increase throttle to lift off.Hover at a safe height.Perform your flight maneuvers.Slowly descend to a safe landing area.Gently lower the drone to the ground.Power off the drone and controller.
Navigation and Maneuvering Techniques
Efficient and safe drone navigation involves understanding how to control the drone in various environments and utilizing advanced features. This includes mastering basic maneuvers and utilizing waypoint systems.
Navigating Different Environments
Flying in different environments requires adapting techniques. Open fields offer ample space, while urban areas necessitate careful navigation around obstacles. Windy conditions require precise control and potentially adjustments to flight plans.
Open fields provide a straightforward flight experience, allowing for greater freedom in maneuvering. Urban areas demand heightened awareness of obstacles like buildings, trees, and power lines. Windy conditions require more skill and may necessitate shortening flights or postponing them entirely.
Waypoints and Automated Flight Planning

Waypoints and automated flight planning simplify complex flights and enable precise aerial photography or videography. These features allow for pre-programmed flight paths, reducing the need for constant manual control.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Waypoints | Pre-defined points in the flight path. The drone autonomously navigates between these points. |
| Automated Flight Planning | Software that allows for the creation of complex flight paths with waypoints, altitude settings, and camera angles. |
Basic Maneuvers
Mastering basic maneuvers is crucial for safe and controlled drone operation. These maneuvers form the foundation for more complex flights.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air. This requires delicate control of the throttle and directional inputs.
- Lateral Movement: Move the drone horizontally (left, right, forward, backward). This involves coordinating throttle and directional inputs.
- Rotation: Rotate the drone around its vertical axis (yaw). This is controlled using the yaw stick or control.
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos involves understanding factors like lighting, composition, and camera settings. Different camera angles significantly impact the visual outcome.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, from basic controls to advanced maneuvers, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help ensure safe and effective drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive flying experience.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Optimal lighting is essential for clear, well-exposed images and videos. Consider the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for soft, warm lighting. Experiment with different camera settings (aperture, shutter speed, ISO) to achieve the desired depth of field and exposure.
Composition plays a key role in creating visually appealing aerial shots. The rule of thirds, leading lines, and symmetry are useful compositional techniques. Avoid placing the subject directly in the center of the frame.
Camera Angles and Visual Effects
Different camera angles create distinct visual effects. Understanding these angles is key to achieving the desired aesthetic.
High Angle Shot (Bird’s-eye view): Provides a broad overview of the scene, emphasizing scale and context. The subject appears smaller, showcasing the surrounding environment.
Low Angle Shot: Emphasizes the size and power of the subject. The subject appears larger and more dominant in the frame.
Dutch Angle (Canted Angle): Creates a sense of unease or disorientation.
The horizon line is tilted, adding a dynamic and dramatic effect.
Stabilizing Footage and Post-Processing
Stabilizing footage is crucial for smooth and professional-looking videos. Many drones have built-in image stabilization systems. Post-processing software can further enhance image quality and correct imperfections.
Software like Adobe Premiere Pro, DaVinci Resolve, and Final Cut Pro offer advanced stabilization tools. Techniques include using stabilization plugins, adjusting keyframes, and applying warp stabilizers. Color grading and sharpening can further enhance the final product.
Battery Management and Maintenance
Proper battery care is crucial for extending battery lifespan and ensuring safe drone operation. This involves correct charging procedures, storage techniques, and troubleshooting common problems.
Battery Care and Charging
Always use the manufacturer-recommended charger. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries completely. Store batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or extreme temperatures. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for optimal battery life.
Overcharging can damage the battery cells, leading to reduced capacity and potential safety hazards. Deep discharging can also damage the battery, reducing its lifespan and performance. Proper storage prevents premature aging and degradation.
Common Battery Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Flight Time | Battery aging, overcharging, or deep discharging | Replace the battery, avoid extreme temperatures, and follow charging guidelines. |
| Swollen Battery | Internal cell damage, overcharging, or short circuit | Immediately discontinue use and replace the battery. Never attempt to repair a swollen battery. |
| Battery Not Charging | Faulty charger, damaged battery contacts, or low battery voltage | Try a different charger, clean the battery contacts, and check the battery voltage. |
Replacing or Upgrading Drone Batteries
Replacing or upgrading drone batteries requires careful handling to avoid damage or injury. Always follow safety precautions.
- Disconnect the battery from the drone before handling.
- Handle batteries carefully, avoiding dropping or puncturing them.
- Use the correct charger for the new battery.
- Dispose of old batteries properly according to local regulations.
Mastering drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. By following the pre-flight checklist, understanding flight controls, and practicing safe maneuvering techniques, you can confidently explore the exciting world of aerial photography and videography. Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to local regulations to ensure a responsible and enjoyable drone flying experience. The sky’s the limit – but always within the bounds of the law!
Commonly Asked Questions: How To Operate A Drone
What is the legal age to operate a drone?
The legal age varies by country and even by specific drone regulations. Check your local laws for the minimum age requirement.
How far can I fly my drone?
The maximum distance depends on your drone’s capabilities, battery life, and local regulations. Always stay within visual line of sight and adhere to any distance restrictions.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this if possible. If not, attempt to manually control the drone back to a safe landing zone.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration is important for accurate flight. It’s generally recommended to calibrate before each flight, especially if you’ve transported your drone or experienced any significant magnetic interference.